Understanding the concept of car drivetrains is an integral part of automobile knowledge. This topic is vital, not just for automobile engineers and mechanics but also for drivers who wish to understand their vehicles better, allowing for improved vehicular maintenance and handling.
A drivetrain, being a pivotal part of a car’s operation, involves numerous components working in unison to provide power from the engine to the wheels. By delving into the intricacies of drivetrain components and their functions, drivers can gain profound insights, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding vehicle maintenance, thereby enhancing the performance and longevity of their vehicles.
Table of Contents
What Is a Drivetrain?
In the realm of automobiles, a drivetrain represents a collection of components working cohesively to transmit power from the vehicle’s engine to its wheels, effectuating motion. This complex system essentially links the engine’s output directly to the wheels and includes elements like the transmission, the driveshaft, the axles, and, of course, the wheels themselves.
Gaining insights into how these components interplay and function in unison not only aids in comprehending the intricate mechanics governing your vehicle’s movement but also allows for a more refined and knowledgeable approach towards driving, maintenance, and troubleshooting, enabling the optimization of the overall vehicular experience.
Types of Drivetrains
There are diverse drivetrain types, each serving distinct driving needs and environments. The primary ones include front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), all-wheel drive (AWD), and four-wheel drive (4WD). In FWD vehicles, the engine power is channeled primarily to the front wheels, rendering it an economical and common choice for most passenger cars. Conversely, RWD systems propel the vehicle by transferring power to the rear wheels, offering enhanced balance and performance, making it a favorite for sports cars and luxury vehicles.
Meanwhile, AWD and 4WD systems provide power to all the vehicle’s wheels to maximize traction and control in various terrains and weather conditions. AWD is always engaged, providing varying power to each wheel as needed, while 4WD can be turned on or off, allowing drivers to switch between two-wheel and four-wheel drive according to the driving conditions.
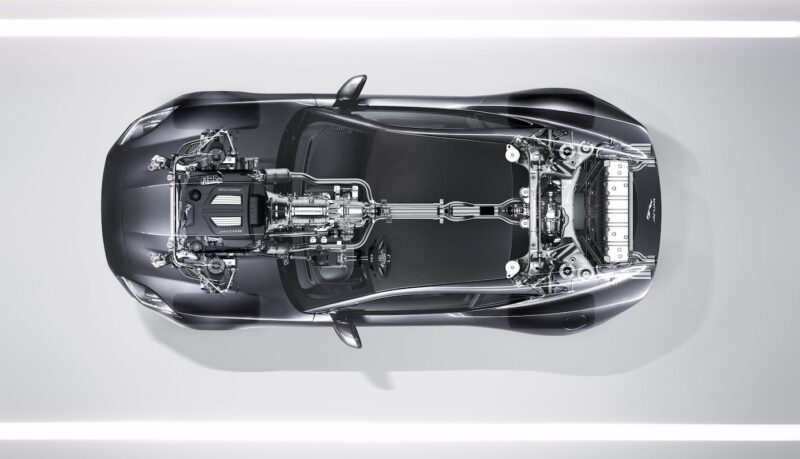
Transmission as a Key Component
Within the drivetrain, the transmission emerges as a key player, serving as the powerhouse manager. It’s responsible for regulating power delivery from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward and backward at various speeds. It performs this through a series of gear ratios that can be manually manipulated in manual transmissions or automatically adjusted in automatic ones.
Understanding the role and workings of the transmission is critical for any driver. It provides insights into the optimal operation of the vehicle and can aid in identifying and resolving issues related to power delivery and vehicle movement, enhancing the overall driving experience and ensuring the longevity and reliability of the vehicle.
The Engine’s Role
The engine is the heart of any vehicle, generating the required power to set the vehicle in motion. It operates by converting fuel into mechanical energy, which is then transferred to the drivetrain, initiating the power transmission to the wheels.
The connection between the engine and the drivetrain is fundamental, and understanding this relationship is crucial for comprehending how cars operate. This knowledge is beneficial not only for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance but also for optimizing the vehicle’s performance and efficiency, leading to a more enriched and informed driving experience.
Components of a Manual Transmission
Manual transmissions, characterized by driver-operated clutches and gearboxes, consist of various components including the clutch, gears, and gearbox. These elements work together to allow the driver to manually select the appropriate gear ratio for the driving conditions, thereby managing the power transmitted from the engine to the wheels. Drivers interact with manual transmissions using the clutch pedal and the gear stick, engaging and disengaging gears to control the vehicle’s speed and torque.
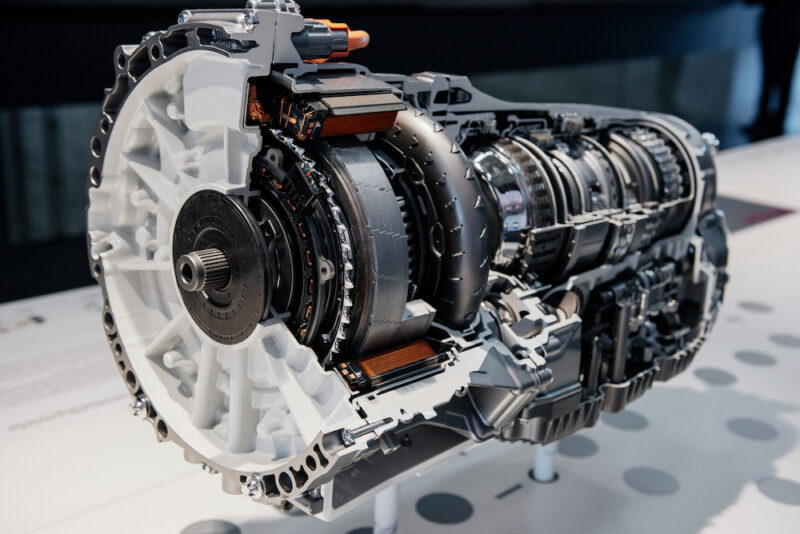
Components of an Automatic Transmission
Automatic transmissions, known for their ease of use, contain components like the torque converter and planetary gearsets. These elements work cohesively to automatically adjust the gear ratios as the vehicle moves, eliminating the need for manual gear shifting. The automatic transmission’s operation is orchestrated by a complex hydraulic system that utilizes fluid pressure to control the gear changes, providing a seamless and user-friendly driving experience.
For those who prioritize convenience and ease in driving, understanding the components and workings of an automatic transmission is invaluable, offering insights into vehicle handling, maintenance, and the optimization of performance and longevity.
Transfer Case in Four-Wheel Drive Systems
Focusing on four-wheel drive systems, the transfer case stands out as a central component. It’s responsible for distributing power from the transmission to both the front and rear axles evenly, enabling balanced and controlled movement in varying terrains.
This component allows for the synchronized operation of all four wheels, which is pivotal in situations demanding enhanced traction and stability. Grasping the function and significance of the transfer case in 4WD systems is essential for drivers navigating challenging terrains, ensuring optimal performance, control, and safety.
Differential ─ Splitting Power
The differential plays a pivotal role in a car’s drivetrain, serving as the component that splits the engine torque two ways, allowing the wheels to spin at different speeds. Since the wheels on a car travel different distances and rotate at different speeds during a turn, the differential is crucial for providing smooth turns and maintaining control. Understanding the differential’s role and operation is essential, as it offers insights into vehicle dynamics and handling, contributing to informed driving, effective troubleshooting, and diligent maintenance, thus enhancing vehicle longevity and performance.
All-Wheel Drive vs. Four-Wheel Drive
When comparing all-wheel drive (AWD) and four-wheel drive (4WD) systems, distinct differences, advantages, and limitations arise. AWD systems are designed to function continuously, providing power to all wheels simultaneously, and adjusting the power distribution as necessary to optimize traction and control in varying conditions.
In contrast, 4WD systems can be manually engaged and disengaged, allowing for a switch between two-wheel and four-wheel operation according to the driver’s needs.
Maintaining the Drivetrain
Maintaining the drivetrain involves a holistic approach focusing on regular inspections, timely fluid changes, and addressing issues promptly. These proactive measures are pivotal in ensuring the optimal functionality and longevity of the drivetrain components.
By conducting regular checks and adhering to maintenance schedules, drivers can preemptively identify and rectify issues, preventing extensive damage and ensuring the seamless operation of the drivetrain. This not only contributes to a more enriched driving experience but also prolongs the lifespan of the vehicle, emphasizing the importance of understanding and maintaining each component of the drivetrain meticulously.

